Mold Remediation is taking action to reduce, isolate, or remove contamination from an environment with the goal of preventing further reproduction and spreading of contaminants. Simply stated, remediation is the process of clean up and disinfection. The overall objective of the remediation process is quite simple: to remove all of the contamination.
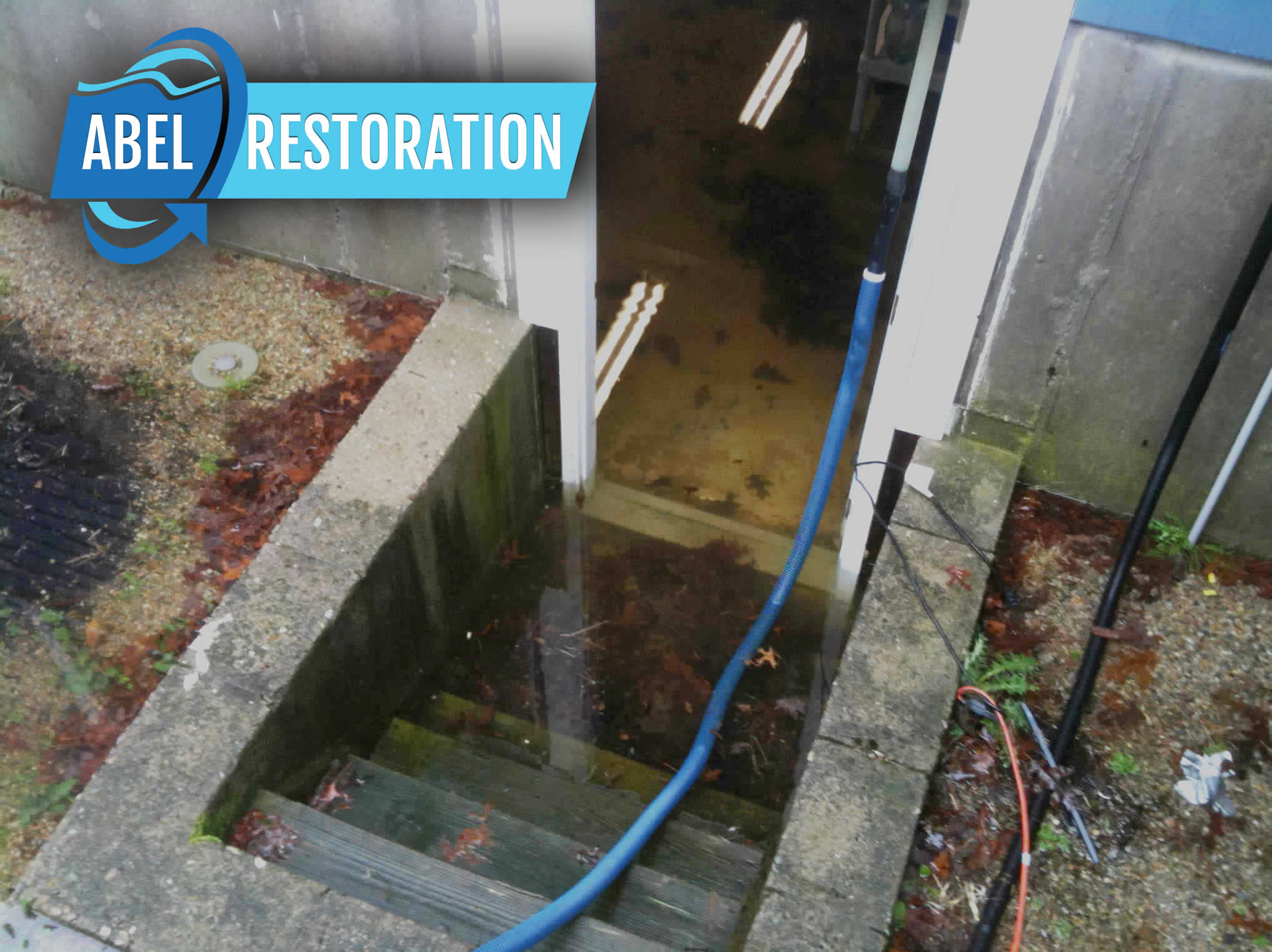
Mold is a microscopic life form found in all parts of the world and is part of the natural decomposition of organic materials. Mold requires three things to grow: nutrients, moisture, and time. The most common food source indoors is cellulose, which is found in wood and drywall. Since Mold requires oxygen, it cannot grow under Water.



Toxic Black Mold
Mycotoxins are toxins that help defend fungi against other microorganisms. It is the mycotoxins produced by fungi that physicians think have negative health consequences on humans. These mycotoxins are found in the cell walls of fungal spores and hyphae. There are actual proteins on the outside of the cell walls that affect whatever they touch.
An easy way to think of them is like the oil that is produced by poison ivy. If you are allergic to poison ivy and touch it, the oil from the plant will create an allergic reaction on your skin. If you are allergic to Mold Damage and ingest it, these proteins will cause a similar allergic reaction inside your body.
Microbial Contamination
Microbial contamination refers to a variety of microorganisms including Mold, bacteria, viruses, protozoa; and fungi, which includes molds, yeasts, and their byproducts and toxins. All of these can affect the health of a building and its occupants. One form of secondary damage – microbial growth – can cause structural components to lose their integrity, can potentially impact indoor air quality, and may ultimately result in compromised occupant health.
The restorer identifies any health concerns arising from pre-existing conditions or from the Water Damage intrusion. Care is taken to contain contaminants and not spread them to unaffected areas of the structure. When dealing with microbial contamination in a structure, the first action is identifying and mitigating safety hazards. We must inspect and be sure any and all safety issues are resolved before moving forward. The next step is to set up containment and control air pressure.
Mold Removal
Mold is a microscopic life form found in all parts of the world It is part of the natural decomposition of organic materials. Mold Damage requires three things to grow: nutrients, moisture, and time. The most common food source indoors is cellulose, which is found in wood and drywall. Mold requires moisture to grow, which means buildings must be kept dry to prevent growth.
The most effective way to prevent Mold growth is to keep materials dry, or if they become wet, to dry them quickly. Remember: no moisture, no Mold. Removing mold involves either removing the Mold Damage from the surface on which it is growing or removing the material where the Mold is growing.
 Call Now: 888-676-1887
Call Now: 888-676-1887

 +1 888-676-1887
+1 888-676-1887
